Financial markets efficiency can be traced back to 1970 when an economist named Eugene Fama developed a theory known as the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH). In the case of an efficient market, it means that all the information has been incorporated into the price and thus it creates an opportunity for those who buy and sell securities to make a profit. Find more information about “Do financial markets operate efficiently?”
What Is Financial Markets Efficiency?
Financial markets efficiency is generally about information and pricing efficiency. It fully and accurately reflects available information about the value of an asset. There are different concepts of financial market efficiency such as its operational efficiency or function. This is entirely inconsistent with the costs that investors can spend on their trades.
It is also inversely related to allocative efficiency, which measures the extent to which a market moves money from lender of last resort to borrower of last resort in such a way that funds are used in the most efficient manner.
A truly efficient market eliminates the possibility of beating the market because whatever information is available to any trader is already included in the market price. As the quality and quantity of information increases, the market becomes more efficient reducing the opportunity for arbitrage and higher market returns.
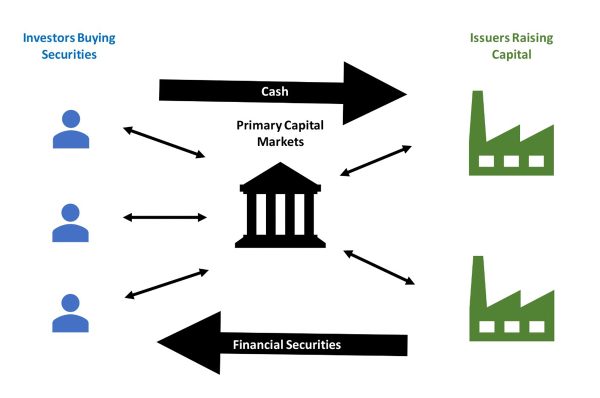
What Types of Efficiency Are There?
Information Arbitrage Efficiency
Arbitrage refers to taking advantage of the similarity in prices of financial instruments between 2 or more markets by trading for a profit.
Arbitrage trading involves only risk-free trades and the source of information for trading is collected free of charge. Since then, profitable opportunities have not been fully exploited, indicating market inefficiencies. This reflects a strong selling efficiency pattern.
Asset prices fully reflect all privately available information. This has the least stringent requirements for efficient markets, since arbitrage includes actionable, risk-free trades.
Fundamental valuation efficiency
Asset prices reflect the expected payment flows associated with holding the asset. Fundamental valuation involves lower risk and less opportunity for profit. It refers to the accuracy of the predicted return on investment.
Financial markets are characterized by predictability and inconsistent bias that force prices to always deviate from their underlying valuation. This reflects a weak information efficiency model.
Understanding Financial Markets Efficiency
A weak form of financial market efficiency is those past price movements are not useful for predicting prices. If this is successful, all relevant information can be collected easily. Therefore, future price changes can only be the result of adding new information.

Under this hypothesis, investment strategies or any technical analysis-based rules used for trading or investment decisions should not be expected to consistently achieve returns in the average normal market. However, this hypothesis can still be profitable through fundamental analysis.
For the strong sell form of the market, stocks adjust quickly to absorb new information, so traders cannot profit from it. This shows that technical and fundamental analysis cannot provide superior returns because any information obtained through fundamental analysis is already available. Only personal information that is not available in the general market will be useful to gain an edge in trading.
What Is Allocative Efficiency?
Allocative Efficiency is one of those states of an economy where the distribution of goods and services is optimal, taking into account consumer preferences.
The price consumers are willing to pay is equivalent to the marginal utility they receive. Hence, the market is producing an output equal to the marginal cost of production. This is allocative efficiency.
What Is Peak Efficiency?
Peak Efficiency is the probability that the quantum will deposit all of its initial energy into the detector. Since there are almost always ways in which a quantum can only accumulate a portion of its energy and then exit the detector, the total efficiency is often greater than the peak efficiency.
What Is Energy Efficiency?
Energy efficiency is the loss of less energy to discharge the same task or produce the same result. Energy-efficient homes and buildings make use of less energy to heat, cool, and electronics and run appliances. At the same time, energy-efficient manufacturing facilities use less energy to produce goods.
Saving energy is one of the easiest and most cost-effective ways to combat climate change, reduce energy costs for consumers, and improve the competitiveness of businesses. Energy efficiency is also a key component to achieving net zero carbon dioxide emissions through decarbonization.

What Are The Impacts of Efficiency?
The nature of the information is not limited to financial news and research. Indeed, information about political, economic, and social events, combined with how investors perceive such information, whether fact or rumor, will be reflected in stock prices. According to EMH, because price only reacts to information available in the market and because all market participants know the same information, no one has the ability to profit from anyone else.
For financial markets efficiency, prices become unpredictable but random so that no investment pattern can be distinguished. Therefore, a planned investment approach cannot succeed.
The random walk of price, often talked about in the EMH school of thought, leads to the failure of any investment strategy that aims to beat the market consistently. In fact, EMH suggests that given the transaction costs associated with portfolio management, it’s more profitable for an investor to put their money in an index fund.
How Do Financial Markets Affect Economic Performance?
To explain the effects of how financial markets affect economic performance, we need more information about the flows of savings and investment. Financial markets efficiency affects the economy by facilitating the accumulation of capital as well as the production of goods and services.
The combination of financial markets development and a variety of products and services needs of lenders and borrowers, especially the whole economy.
Financial Markets, instruments, and institutions provide an opportunity for investors to specialize in specific markets or services or both. As noted by Demirguc-Kunt and Levine, financial markets and financial institutions jointly contribute to economic growth. The relative combination of the two doesn’t seem to be an important factor in growth.
How Do You Calculate Financial markets Efficiency?
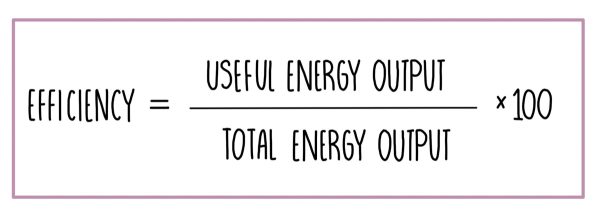
The way to calculate and determine the main financial markets efficiency is based on the percentage keeping output and input. The standard formula for efficiency is Efficiency = Output / Input then multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
η=Eout/Ein x 100%
with:
- η is the efficiency (expressed as a percentage)
- Eout is the energy output
- Ein is the energy input
Any efficiency calculated from real-world values will be between 0% and 100%.
- An efficiency of 0% means that all the input energy is wasted, and the energy output is equal to zero
- On the other hand, an efficiency of 100% means that there is no waste of energy whatsoever
Example of Financial Markets Efficiency
In those cases where certain stocks are added to an index like the S&P 500 for the first time, there will be a big boost to that stock’s price simply because it becomes part of the index rather than the stock price, not because of any new changes in the company’s fundamentals.
This stat effect anomaly has been widely reported and known. So most of it is gone. This means that when information increases, markets get more efficient and anomalies are reduced.
What Is a Measure of Efficiency in an Investment?
Tracking and choosing a measurement method is also important for your portfolio. As time goes by, you will have to make an assessment of the status of the investment. If it is progressing, the portfolio value is increasing gradually. Conversely, if the investments are not profitable or are trending down, you need to identify the cause of that result.
In addition, the ever-changing market keeps you alert and looking for other opportunities to improve your portfolio or diversify by allocating to other investment areas. To free up money to make these new purchases, you may want to sell individual investments that aren’t performing well, while not giving up your chosen asset allocation when appropriate.
The Bottom Line
Financial markets efficiency is a measurement process that plays an important role in your portfolio. Therefore, understanding “Do financial markets operate efficiently” is essential to improve investments. We also provide many articles related to financial markets, stay tuned for more updates!



