1. Getting Started
These are the top 5 butterfly spread option strategy, always chosen by the professionals for maximizing their profits in a neutral market. Unlike trading equity in more traditional financial markets, options trading utilizes a form of derivative contracts that grants both buyer and seller new approaches to making profits. However, trading with this kind of financial instrument is not something that is too common and intuitive for any trader to understand.
The concept of trading derivatives is already complex. But to actually make consistent flows of trading profits from options contracts, you have to understand how a certain strategy like a butterfly spread works and can be applied in your trading system. And that is a whole different story. Learners are recommended to have a comprehensive overview of options trading so that they will not get overwhelmed and be able to get the hang of these 5 following essential butterfly spread options strategies.
2. Butterfly Spread Definition
What is a Spread?
Generally speaking, a spread refers to the difference between two specific financial values. They can either be two prices, rates, yields, and so on. The bid-ask spread is one of the most common types of spreads, referring to the distance between the bid and the ask prices of a certain financial instrument.
When it comes to options trading or futures trading. The spread can also refer to the gap in a trading position – between a short position (selling) in one options contract and a long position (buying) in another.
What is a Butterfly Spread?
In finance, a Butterfly Spread options strategy is a non-directional strategy that is designed to benefit from little movements of the market and utilized to significantly increase the probability of winning trades while limiting all the lurking risks. During such a strategy, users usually expect the future volatility of the underlying assets to be either lower (when long) or greater (when short) than the current state of the implied volatility.
Like other options trading strategies, the butterfly spreads utilize derivatives or contracts that connect to a certain type of financial instruments – also known as the underlying assets when talking about the contracts themselves. Options trading usually involves stocks or commodities as financial instruments.
A butterfly spread option strategy can be regarded as the combination of both a bear spread and a bull spread and applied in a neutral market expected with little movement. A basic butterfly spread usually contains four options contracts with the same expiration date and three different strike prices – a high one, an at-the-money one, and a lower one.
Two outer strike prices both have the same gap value when compared to that of the at-the-money contract. For instance, if the strike price of the at-the-money option is $50, the values of the other two will consecutively be $45 and $55. Both are $5 away from the middle one.
Combining the basic butterfly spread with puts and calls will create more varieties of butter spreads and new approaches to benefit yourself from trading options contracts while being adaptable to any extent of volatility.
3. Type of Butterfly Spread Option Strategy
Long Butterfly Spread With Puts
The long butterfly spread with puts setup:
- Sell two at-the-money put options (strike price B)
- Buy an in-the-money put option with a lower value (strike price A)
- Buy an out-of-the-money put option with a higher value (strike price C)
- All contracts have the same expiration date
As the strategy benefits from the stability of the market movements, the long butterfly spread with puts reaches its potential when the stock price is at the same value as that of written puts at the expiration date. The option buyer will then have a chance to receive a maximum profit that is equal to the strike price C minus strike price B and any premium or commission paid.
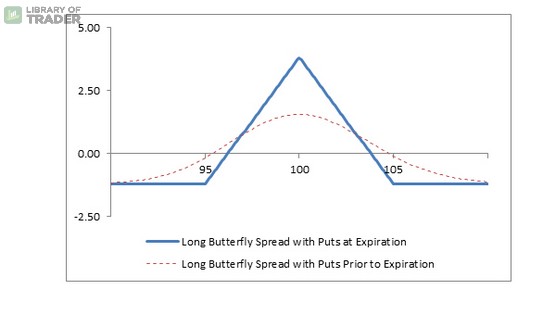
If you manage to make the right prediction that the stock price will stay close strike price B, you want the future volatility to decrease as significantly as it can. As a result, if you approach the strategy when the stock price is somewhere outside of strike price A or C. You want the future volatility to strike hard so that it can make remarkable movements, helping the stock price get to an in-the-money position.
Long Butterfly Spread With Calls
The long butterfly spread with calls setup:
- Sell two at-the-money call options (strike price B)
- Buy an in-the-money call option with a lower value (strike price A)
- Buy an out-of-the-money call option with a higher value (strike price C)
- All contracts have the same expiration date
Just like the long butterfly spread with puts, this strategy is expected to reach the highest profitability as long as the stock price stays close to the strike price B. In short, the closer they are, the lower volatility should be, and vice versa.
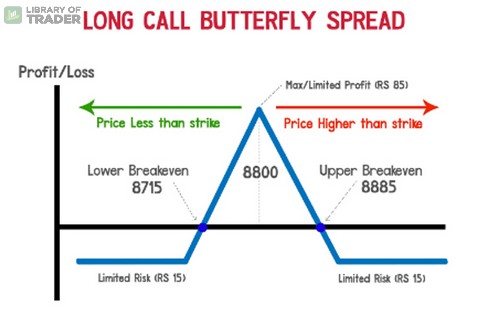
The attractive yield from using a long butterfly spread with calls is limited to strike price B minus strike price A and any premium or commission paid. As time goes by, you will want the ideal situation where all options – except the call at strike price A – expire worthless with the stock price hitting the same value as strike price B.
Short Butterfly Spread With Puts
Short butterfly spread with puts setup:
- Buy two at-the-money put options (strike price B)
- Sell an in-the-money put option with a lower value (strike price A)
- Sell an out-of-the-money put option with a higher value (strike price C)
- All contracts have the same expiration date
This kind of butterfly spread is obviously the reverse version of the two aforementioned strategies. To realize the maximum profit with this approach, you – the option writers – will want the price of the underlying asset to stay outside the two outer strike prices (A and C). The gains are the premiums paid by the option buyers. The loss is only limited to the amount calculated by having strike price C minus strike price B as well as the premiums received.
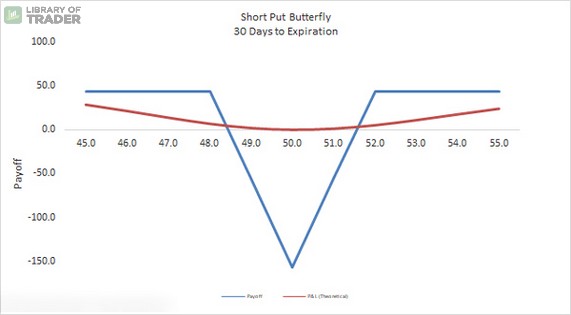
The expected future volatility depends on the current position of the stock price, compared with the strike price B. If the price of the underlying stock is somewhere between strike price A and strike price C, you should expect the high volatility to hit, so that it can get the stock price out of an unfavorable position. If the stock price is already lower than strike price A or higher than strike price C, the more insignificant the movements are, the better.
Short Butterfly Spread With Calls
Short butterfly spread with calls setup:
- Buy two at-the-money call options (strike price B)
- Sell an in-the-money call option with a lower value (strike price A)
- Sell an out-of-the-money call option with a higher value (strike price C)
- All contracts have the same expiration date
In this version of the short butterfly spread, we utilize calls instead of puts to be more adaptable to the movements of the market. A net credit is usually created as the trader initiates the contract. Just like its counterpart of short butterfly spreads, this strategy achieves its full profitability if the stock price manages to go anywhere else except for the gap between strike price A and strike price C.

In such an ideal situation, the option writer will receive his maximum profits in the form of premiums paid by the buyers. Otherwise, that trader only gets a loss that is limited to the amount calculated by having strike price B minus strike price A as well as the premium received. High future volatility should also be expected if the stock price stays too close to the strike price B. You will the market to make strong movements to get it out of this unfavorable position.
Iron Butterfly Spread
Iron butterfly spread setup:
- Sell an at-the-money put option (strike price B)
- Sell an at-the-money call option (strike price B)
- Buy an out-of-the-money put option with a lower value (strike price A)
- Buy an out-of-the-money call option with a higher value (strike price C)
- All contracts have the same expiration date

The iron butterfly utilizes both calls and puts to create one more version of butterfly spreads for traders to consider in their trading system. This strategy is best suited for a neutral market with an insignificant state of volatility. If the price of the underlying manages to stay as close to the strike price B as possible, the trader who initiated this strategy will receive premiums as his gains.
The potential losses from the iron butterfly are limited to the amount calculated by having strike price C of the bought call option minus strike price B of the written call option as well as any premium received. As for the expected volatility, you should anticipate a certain number of changes to get the stock price to stay close to strike price B for maximum potential earnings.
4. In conclusion
At first glance, the butterfly spread option strategy share significant similarities that can easily get newcomers greatly confused. But if you actually take your time to digest the information, you will soon come to find out that each strategy is tailored to making the most out of certain situations. What is left for you to do is identify those opportunities and make your decisions to seize your deserved earnings.


